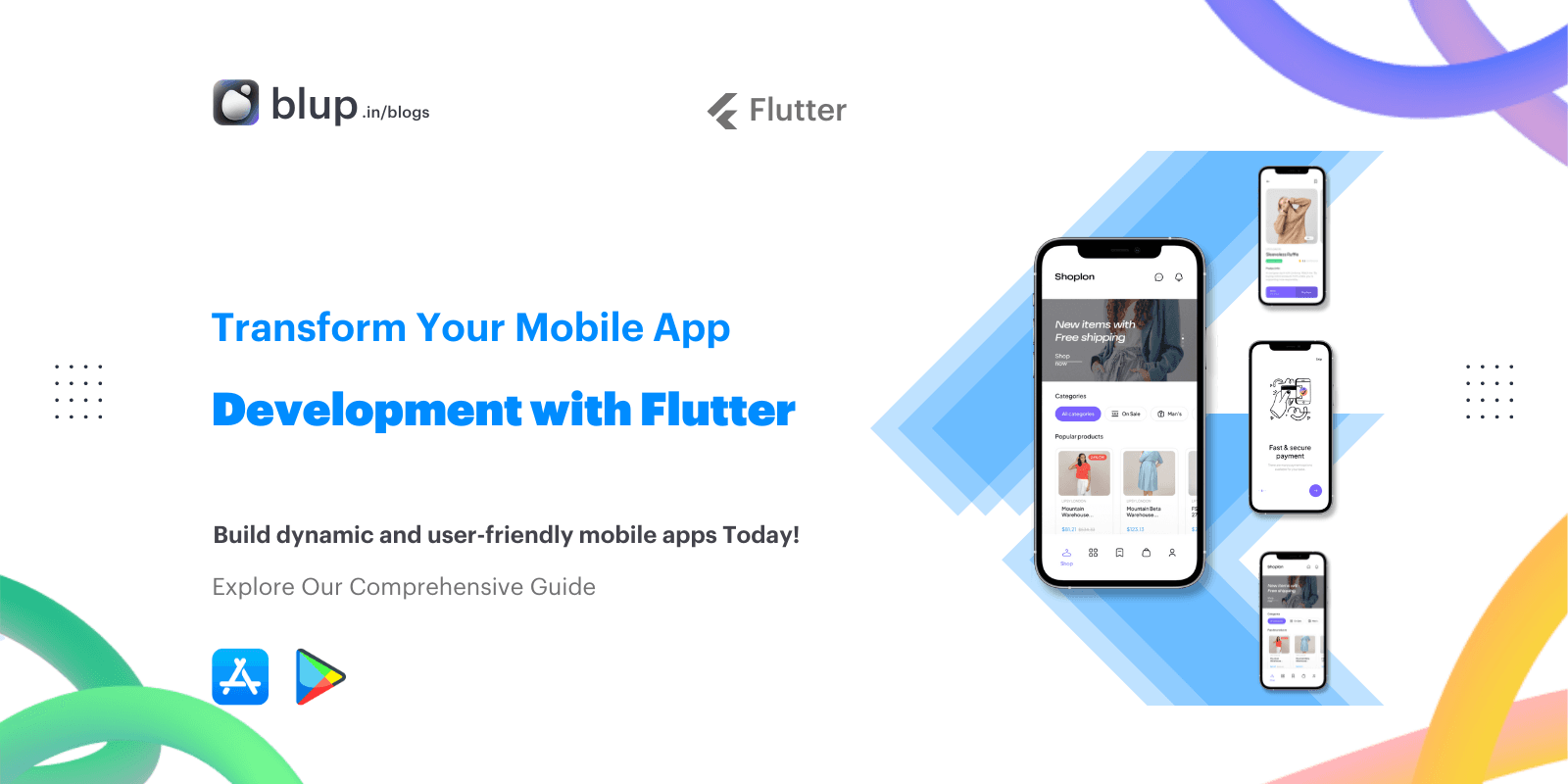
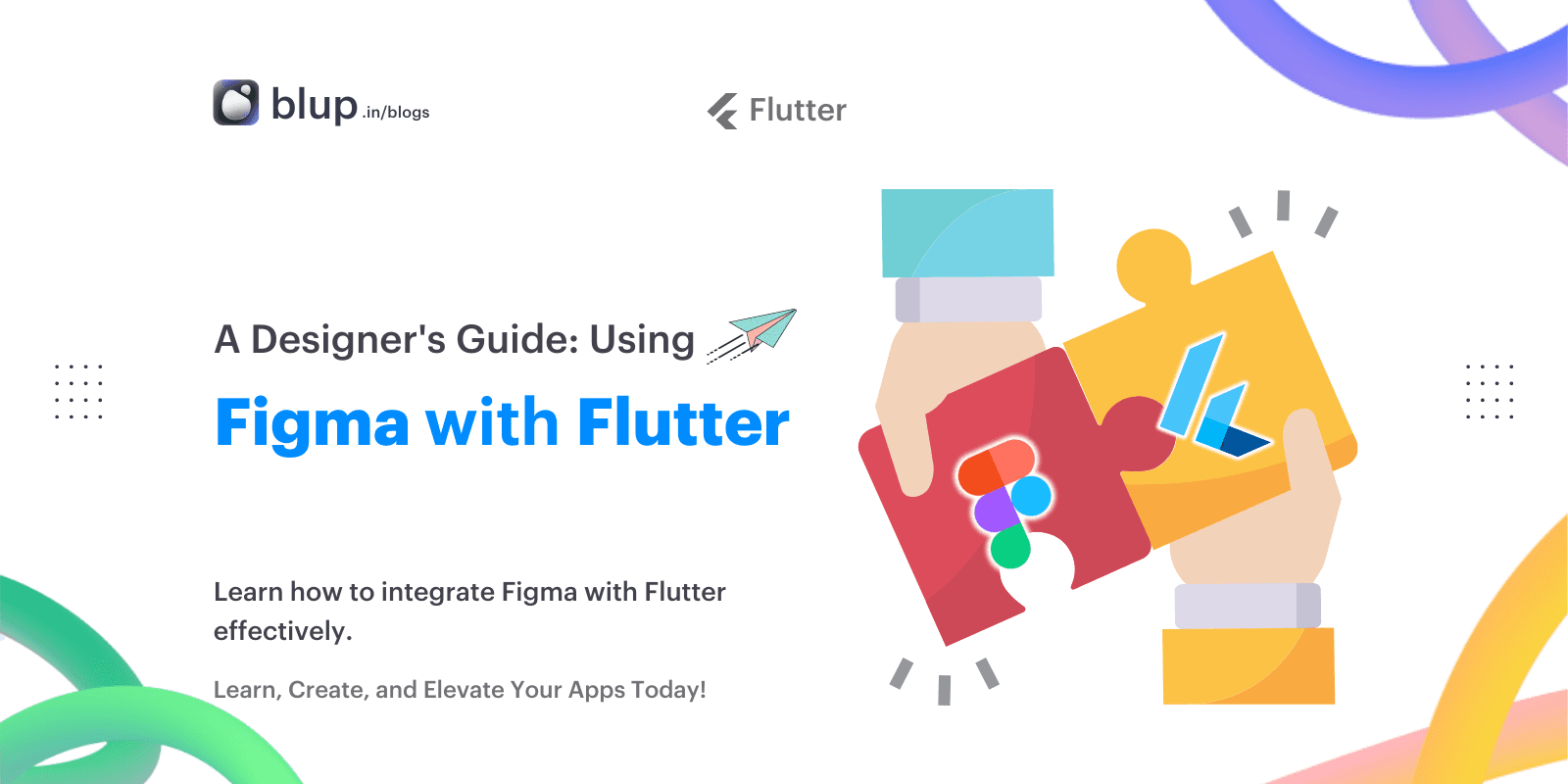
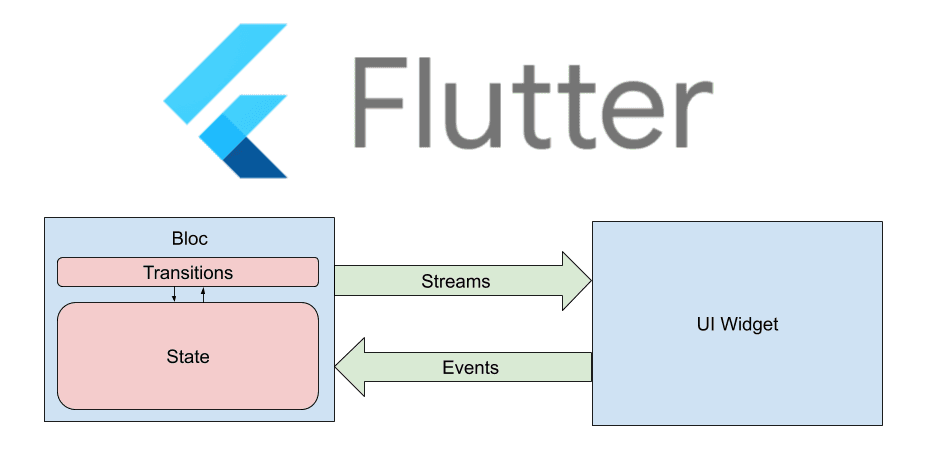
How to Build Enterprise-Grade Software with Low-Code Platforms.

Introduction
Introduction
Introduction
Introduction
Overview
Low-code platforms have revolutionized the way enterprises develop software by simplifying the development process and accelerating time-to-market. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how to leverage low-code platforms to build enterprise-grade software efficiently.
Benefits
Low-code platforms offer several benefits, including:
Faster Development: Rapid prototyping and development through visual interfaces.
Reduced Costs: Lower development and maintenance costs.
Scalability: Easily scalable solutions that can grow with your business.
Enhanced Collaboration: Improved collaboration between business and IT teams.
Overview
Low-code platforms have revolutionized the way enterprises develop software by simplifying the development process and accelerating time-to-market. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how to leverage low-code platforms to build enterprise-grade software efficiently.
Benefits
Low-code platforms offer several benefits, including:
Faster Development: Rapid prototyping and development through visual interfaces.
Reduced Costs: Lower development and maintenance costs.
Scalability: Easily scalable solutions that can grow with your business.
Enhanced Collaboration: Improved collaboration between business and IT teams.
Overview
Low-code platforms have revolutionized the way enterprises develop software by simplifying the development process and accelerating time-to-market. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how to leverage low-code platforms to build enterprise-grade software efficiently.
Benefits
Low-code platforms offer several benefits, including:
Faster Development: Rapid prototyping and development through visual interfaces.
Reduced Costs: Lower development and maintenance costs.
Scalability: Easily scalable solutions that can grow with your business.
Enhanced Collaboration: Improved collaboration between business and IT teams.
Overview
Low-code platforms have revolutionized the way enterprises develop software by simplifying the development process and accelerating time-to-market. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how to leverage low-code platforms to build enterprise-grade software efficiently.
Benefits
Low-code platforms offer several benefits, including:
Faster Development: Rapid prototyping and development through visual interfaces.
Reduced Costs: Lower development and maintenance costs.
Scalability: Easily scalable solutions that can grow with your business.
Enhanced Collaboration: Improved collaboration between business and IT teams.
Understanding Low-Code Platforms
Understanding Low-Code Platforms
Understanding Low-Code Platforms
Understanding Low-Code Platforms
What Are Low-Code Platforms?
Low-code platforms are development environments that enable the creation of applications through graphical user interfaces and configuration rather than traditional hand-coded programming. They allow developers to build applications quickly with minimal manual coding.
Key Features
Key features of low-code platforms include:
Visual Development: Drag-and-drop interface for building applications.
Reusable Components: Pre-built templates and components.
Integration Capabilities: Easy integration with existing systems and databases.
Workflow Automation: Tools to automate business processes.
What Are Low-Code Platforms?
Low-code platforms are development environments that enable the creation of applications through graphical user interfaces and configuration rather than traditional hand-coded programming. They allow developers to build applications quickly with minimal manual coding.
Key Features
Key features of low-code platforms include:
Visual Development: Drag-and-drop interface for building applications.
Reusable Components: Pre-built templates and components.
Integration Capabilities: Easy integration with existing systems and databases.
Workflow Automation: Tools to automate business processes.
What Are Low-Code Platforms?
Low-code platforms are development environments that enable the creation of applications through graphical user interfaces and configuration rather than traditional hand-coded programming. They allow developers to build applications quickly with minimal manual coding.
Key Features
Key features of low-code platforms include:
Visual Development: Drag-and-drop interface for building applications.
Reusable Components: Pre-built templates and components.
Integration Capabilities: Easy integration with existing systems and databases.
Workflow Automation: Tools to automate business processes.
What Are Low-Code Platforms?
Low-code platforms are development environments that enable the creation of applications through graphical user interfaces and configuration rather than traditional hand-coded programming. They allow developers to build applications quickly with minimal manual coding.
Key Features
Key features of low-code platforms include:
Visual Development: Drag-and-drop interface for building applications.
Reusable Components: Pre-built templates and components.
Integration Capabilities: Easy integration with existing systems and databases.
Workflow Automation: Tools to automate business processes.
Choosing the Right Low-Code Platform
Choosing the Right Low-Code Platform
Choosing the Right Low-Code Platform
Choosing the Right Low-Code Platform
Evaluation Criteria
When choosing a low-code platform for enterprise needs, consider the following factors:
Scalability: Can the platform handle your organization's growth?
Security: Does it offer robust security features?
Integration: Can it easily integrate with your existing systems?
Customization: How flexible is it in terms of customization?

Popular Platforms
Some of the leading low-code platforms include:
Blup: Drag-and-drop interface for building applications, Pre-built templates, and components.
FlutterFlow: Known for its scalability and integration capabilities.
Mendix: Offers extensive tools for rapid development and deployment.
Microsoft Power Apps: Integrates well with other Microsoft products.
Appian: Focuses on process automation and enterprise-grade applications.
Evaluation Criteria
When choosing a low-code platform for enterprise needs, consider the following factors:
Scalability: Can the platform handle your organization's growth?
Security: Does it offer robust security features?
Integration: Can it easily integrate with your existing systems?
Customization: How flexible is it in terms of customization?

Popular Platforms
Some of the leading low-code platforms include:
Blup: Drag-and-drop interface for building applications, Pre-built templates, and components.
FlutterFlow: Known for its scalability and integration capabilities.
Mendix: Offers extensive tools for rapid development and deployment.
Microsoft Power Apps: Integrates well with other Microsoft products.
Appian: Focuses on process automation and enterprise-grade applications.
Evaluation Criteria
When choosing a low-code platform for enterprise needs, consider the following factors:
Scalability: Can the platform handle your organization's growth?
Security: Does it offer robust security features?
Integration: Can it easily integrate with your existing systems?
Customization: How flexible is it in terms of customization?

Popular Platforms
Some of the leading low-code platforms include:
Blup: Drag-and-drop interface for building applications, Pre-built templates, and components.
FlutterFlow: Known for its scalability and integration capabilities.
Mendix: Offers extensive tools for rapid development and deployment.
Microsoft Power Apps: Integrates well with other Microsoft products.
Appian: Focuses on process automation and enterprise-grade applications.
Evaluation Criteria
When choosing a low-code platform for enterprise needs, consider the following factors:
Scalability: Can the platform handle your organization's growth?
Security: Does it offer robust security features?
Integration: Can it easily integrate with your existing systems?
Customization: How flexible is it in terms of customization?

Popular Platforms
Some of the leading low-code platforms include:
Blup: Drag-and-drop interface for building applications, Pre-built templates, and components.
FlutterFlow: Known for its scalability and integration capabilities.
Mendix: Offers extensive tools for rapid development and deployment.
Microsoft Power Apps: Integrates well with other Microsoft products.
Appian: Focuses on process automation and enterprise-grade applications.
Planning Your Enterprise Software Project
Planning Your Enterprise Software Project
Planning Your Enterprise Software Project
Planning Your Enterprise Software Project
Requirement Gathering
Effective requirement gathering involves:
Stakeholder Interviews: Engage with stakeholders to understand their needs.
Workshops: Conduct workshops to gather detailed requirements.
Documentation: Document all requirements clearly and concisely.
Project Scope and Goals
Define the scope and goals by:
Setting Clear Objectives: Determine what the application needs to achieve.
Identifying Constraints: Recognize any limitations or constraints.
Creating a Roadmap: Develop a project roadmap with milestones and timelines.
Requirement Gathering
Effective requirement gathering involves:
Stakeholder Interviews: Engage with stakeholders to understand their needs.
Workshops: Conduct workshops to gather detailed requirements.
Documentation: Document all requirements clearly and concisely.
Project Scope and Goals
Define the scope and goals by:
Setting Clear Objectives: Determine what the application needs to achieve.
Identifying Constraints: Recognize any limitations or constraints.
Creating a Roadmap: Develop a project roadmap with milestones and timelines.
Requirement Gathering
Effective requirement gathering involves:
Stakeholder Interviews: Engage with stakeholders to understand their needs.
Workshops: Conduct workshops to gather detailed requirements.
Documentation: Document all requirements clearly and concisely.
Project Scope and Goals
Define the scope and goals by:
Setting Clear Objectives: Determine what the application needs to achieve.
Identifying Constraints: Recognize any limitations or constraints.
Creating a Roadmap: Develop a project roadmap with milestones and timelines.
Requirement Gathering
Effective requirement gathering involves:
Stakeholder Interviews: Engage with stakeholders to understand their needs.
Workshops: Conduct workshops to gather detailed requirements.
Documentation: Document all requirements clearly and concisely.
Project Scope and Goals
Define the scope and goals by:
Setting Clear Objectives: Determine what the application needs to achieve.
Identifying Constraints: Recognize any limitations or constraints.
Creating a Roadmap: Develop a project roadmap with milestones and timelines.
Designing the Application
Designing the Application
Designing the Application
Designing the Application
User Interface (UI) Design
Best practices for UI design include:
Consistency: Maintain consistency in design elements.
Simplicity: Keep the interface simple and intuitive.
Accessibility: Ensure the application is accessible to all users.
User Experience (UX) Considerations
Optimize UX by:
Conducting User Research: Understand the needs and behaviors of your users.
Prototyping and Testing: Create prototypes and conduct usability testing.
Iterative Design: Continuously improve the design based on user feedback.
User Interface (UI) Design
Best practices for UI design include:
Consistency: Maintain consistency in design elements.
Simplicity: Keep the interface simple and intuitive.
Accessibility: Ensure the application is accessible to all users.
User Experience (UX) Considerations
Optimize UX by:
Conducting User Research: Understand the needs and behaviors of your users.
Prototyping and Testing: Create prototypes and conduct usability testing.
Iterative Design: Continuously improve the design based on user feedback.
User Interface (UI) Design
Best practices for UI design include:
Consistency: Maintain consistency in design elements.
Simplicity: Keep the interface simple and intuitive.
Accessibility: Ensure the application is accessible to all users.
User Experience (UX) Considerations
Optimize UX by:
Conducting User Research: Understand the needs and behaviors of your users.
Prototyping and Testing: Create prototypes and conduct usability testing.
Iterative Design: Continuously improve the design based on user feedback.
User Interface (UI) Design
Best practices for UI design include:
Consistency: Maintain consistency in design elements.
Simplicity: Keep the interface simple and intuitive.
Accessibility: Ensure the application is accessible to all users.
User Experience (UX) Considerations
Optimize UX by:
Conducting User Research: Understand the needs and behaviors of your users.
Prototyping and Testing: Create prototypes and conduct usability testing.
Iterative Design: Continuously improve the design based on user feedback.
Developing with Low-Code Platforms
Developing with Low-Code Platforms
Developing with Low-Code Platforms
Developing with Low-Code Platforms
Drag-and-Drop Interfaces
Utilize drag-and-drop features to:
Quickly Build Layouts: Assemble application layouts with ease.
Use Pre-Built Components: Incorporate ready-made components to save time.
Customize as Needed: Adjust components to fit specific requirements.
Custom Code Integration
Integrate custom code to:
Extend Functionality: Add unique features not available in the low-code platform.
Integrate APIs: Connect with external services and APIs.
Enhance Performance: Optimize performance through custom solutions.
Drag-and-Drop Interfaces
Utilize drag-and-drop features to:
Quickly Build Layouts: Assemble application layouts with ease.
Use Pre-Built Components: Incorporate ready-made components to save time.
Customize as Needed: Adjust components to fit specific requirements.
Custom Code Integration
Integrate custom code to:
Extend Functionality: Add unique features not available in the low-code platform.
Integrate APIs: Connect with external services and APIs.
Enhance Performance: Optimize performance through custom solutions.
Drag-and-Drop Interfaces
Utilize drag-and-drop features to:
Quickly Build Layouts: Assemble application layouts with ease.
Use Pre-Built Components: Incorporate ready-made components to save time.
Customize as Needed: Adjust components to fit specific requirements.
Custom Code Integration
Integrate custom code to:
Extend Functionality: Add unique features not available in the low-code platform.
Integrate APIs: Connect with external services and APIs.
Enhance Performance: Optimize performance through custom solutions.
Drag-and-Drop Interfaces
Utilize drag-and-drop features to:
Quickly Build Layouts: Assemble application layouts with ease.
Use Pre-Built Components: Incorporate ready-made components to save time.
Customize as Needed: Adjust components to fit specific requirements.
Custom Code Integration
Integrate custom code to:
Extend Functionality: Add unique features not available in the low-code platform.
Integrate APIs: Connect with external services and APIs.
Enhance Performance: Optimize performance through custom solutions.
Ensuring Security and Compliance
Ensuring Security and Compliance
Ensuring Security and Compliance
Ensuring Security and Compliance
Security Best Practices
Implement key security practices such as:
Data Encryption: Encrypt data in transit and at rest.
Authentication and Authorization: Use strong authentication and authorization mechanisms.
Regular Audits: Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments.
Compliance Requirements
Ensure compliance with regulations by:
Understanding Legal Requirements: Know the relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
Implementing Policies: Develop and implement compliance policies.
Monitoring and Reporting: Continuously monitor compliance and report any issues.
Security Best Practices
Implement key security practices such as:
Data Encryption: Encrypt data in transit and at rest.
Authentication and Authorization: Use strong authentication and authorization mechanisms.
Regular Audits: Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments.
Compliance Requirements
Ensure compliance with regulations by:
Understanding Legal Requirements: Know the relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
Implementing Policies: Develop and implement compliance policies.
Monitoring and Reporting: Continuously monitor compliance and report any issues.
Security Best Practices
Implement key security practices such as:
Data Encryption: Encrypt data in transit and at rest.
Authentication and Authorization: Use strong authentication and authorization mechanisms.
Regular Audits: Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments.
Compliance Requirements
Ensure compliance with regulations by:
Understanding Legal Requirements: Know the relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
Implementing Policies: Develop and implement compliance policies.
Monitoring and Reporting: Continuously monitor compliance and report any issues.
Security Best Practices
Implement key security practices such as:
Data Encryption: Encrypt data in transit and at rest.
Authentication and Authorization: Use strong authentication and authorization mechanisms.
Regular Audits: Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments.
Compliance Requirements
Ensure compliance with regulations by:
Understanding Legal Requirements: Know the relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
Implementing Policies: Develop and implement compliance policies.
Monitoring and Reporting: Continuously monitor compliance and report any issues.
Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing Strategies
Effective testing strategies include:
Unit Testing: Test individual components for functionality.
Integration Testing: Ensure that different parts of the application work together seamlessly.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Validate the application with end-users.
Continuous Integration and Delivery (CI/CD)
Implement CI/CD for:
Automated Testing: Run automated tests to detect issues early.
Continuous Deployment: Deploy updates and new features continuously.
Monitoring and Feedback: Monitor performance and gather feedback for improvements
Testing Strategies
Effective testing strategies include:
Unit Testing: Test individual components for functionality.
Integration Testing: Ensure that different parts of the application work together seamlessly.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Validate the application with end-users.
Continuous Integration and Delivery (CI/CD)
Implement CI/CD for:
Automated Testing: Run automated tests to detect issues early.
Continuous Deployment: Deploy updates and new features continuously.
Monitoring and Feedback: Monitor performance and gather feedback for improvements
Testing Strategies
Effective testing strategies include:
Unit Testing: Test individual components for functionality.
Integration Testing: Ensure that different parts of the application work together seamlessly.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Validate the application with end-users.
Continuous Integration and Delivery (CI/CD)
Implement CI/CD for:
Automated Testing: Run automated tests to detect issues early.
Continuous Deployment: Deploy updates and new features continuously.
Monitoring and Feedback: Monitor performance and gather feedback for improvements
Testing Strategies
Effective testing strategies include:
Unit Testing: Test individual components for functionality.
Integration Testing: Ensure that different parts of the application work together seamlessly.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Validate the application with end-users.
Continuous Integration and Delivery (CI/CD)
Implement CI/CD for:
Automated Testing: Run automated tests to detect issues early.
Continuous Deployment: Deploy updates and new features continuously.
Monitoring and Feedback: Monitor performance and gather feedback for improvements
Deployment and Maintenance
Deployment and Maintenance
Deployment and Maintenance
Deployment and Maintenance
Deployment Process
Steps for deploying your application:
Staging Environment: Use a staging environment to test deployment.
Deployment Checklist: Follow a checklist to ensure all steps are completed.
Go Live: Deploy the application to the production environment.
Ongoing Maintenance
Maintain your application by:
Regular Updates: Release updates to fix bugs and add features.
Performance Monitoring: Continuously monitor application performance.
User Support: Provide support to users and address their issues promptly.
Deployment Process
Steps for deploying your application:
Staging Environment: Use a staging environment to test deployment.
Deployment Checklist: Follow a checklist to ensure all steps are completed.
Go Live: Deploy the application to the production environment.
Ongoing Maintenance
Maintain your application by:
Regular Updates: Release updates to fix bugs and add features.
Performance Monitoring: Continuously monitor application performance.
User Support: Provide support to users and address their issues promptly.
Deployment Process
Steps for deploying your application:
Staging Environment: Use a staging environment to test deployment.
Deployment Checklist: Follow a checklist to ensure all steps are completed.
Go Live: Deploy the application to the production environment.
Ongoing Maintenance
Maintain your application by:
Regular Updates: Release updates to fix bugs and add features.
Performance Monitoring: Continuously monitor application performance.
User Support: Provide support to users and address their issues promptly.
Deployment Process
Steps for deploying your application:
Staging Environment: Use a staging environment to test deployment.
Deployment Checklist: Follow a checklist to ensure all steps are completed.
Go Live: Deploy the application to the production environment.
Ongoing Maintenance
Maintain your application by:
Regular Updates: Release updates to fix bugs and add features.
Performance Monitoring: Continuously monitor application performance.
User Support: Provide support to users and address their issues promptly.
Conclusion
Conclusion
Conclusion
Conclusion
Recap
We've covered the essential steps for building enterprise-grade software using low-code platforms, from understanding the platforms to deployment and maintenance.
Future Trends
Future trends in low-code platforms include AI integration, enhanced automation, and increased focus on user experience.
Call to Action
Start exploring low-code platforms today and build robust enterprise applications that drive your business forward.
Recap
We've covered the essential steps for building enterprise-grade software using low-code platforms, from understanding the platforms to deployment and maintenance.
Future Trends
Future trends in low-code platforms include AI integration, enhanced automation, and increased focus on user experience.
Call to Action
Start exploring low-code platforms today and build robust enterprise applications that drive your business forward.
Recap
We've covered the essential steps for building enterprise-grade software using low-code platforms, from understanding the platforms to deployment and maintenance.
Future Trends
Future trends in low-code platforms include AI integration, enhanced automation, and increased focus on user experience.
Call to Action
Start exploring low-code platforms today and build robust enterprise applications that drive your business forward.
Recap
We've covered the essential steps for building enterprise-grade software using low-code platforms, from understanding the platforms to deployment and maintenance.
Future Trends
Future trends in low-code platforms include AI integration, enhanced automation, and increased focus on user experience.
Call to Action
Start exploring low-code platforms today and build robust enterprise applications that drive your business forward.
Table of content
© 2021-25 Blupx Private Limited.
All rights reserved.
© 2021-25 Blupx Private Limited.
All rights reserved.
© 2021-25 Blupx Private Limited.
All rights reserved.