Ultimate Guide to Flutter App Development


Introduction
Introduction
Introduction
Introduction
Flutter, developed by Google, is an open-source UI software development kit used to create beautiful, natively compiled applications for mobile, web, and desktop from a single codebase. This guide is designed to take you through the journey of Flutter app development, whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer looking to enhance your skills.
Why Choose Flutter
Flutter stands out for several reasons:
Fast Development: Hot reload allows you to see changes in real time.
Expressive and Flexible UI: Customizable widgets make it easy to build beautiful UIs.
Native Performance: Flutter’s compilation of native ARM code ensures high performance.
Flutter, developed by Google, is an open-source UI software development kit used to create beautiful, natively compiled applications for mobile, web, and desktop from a single codebase. This guide is designed to take you through the journey of Flutter app development, whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer looking to enhance your skills.
Why Choose Flutter
Flutter stands out for several reasons:
Fast Development: Hot reload allows you to see changes in real time.
Expressive and Flexible UI: Customizable widgets make it easy to build beautiful UIs.
Native Performance: Flutter’s compilation of native ARM code ensures high performance.
Flutter, developed by Google, is an open-source UI software development kit used to create beautiful, natively compiled applications for mobile, web, and desktop from a single codebase. This guide is designed to take you through the journey of Flutter app development, whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer looking to enhance your skills.
Why Choose Flutter
Flutter stands out for several reasons:
Fast Development: Hot reload allows you to see changes in real time.
Expressive and Flexible UI: Customizable widgets make it easy to build beautiful UIs.
Native Performance: Flutter’s compilation of native ARM code ensures high performance.
Flutter, developed by Google, is an open-source UI software development kit used to create beautiful, natively compiled applications for mobile, web, and desktop from a single codebase. This guide is designed to take you through the journey of Flutter app development, whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer looking to enhance your skills.
Why Choose Flutter
Flutter stands out for several reasons:
Fast Development: Hot reload allows you to see changes in real time.
Expressive and Flexible UI: Customizable widgets make it easy to build beautiful UIs.
Native Performance: Flutter’s compilation of native ARM code ensures high performance.
Getting Started with Flutter
Getting Started with Flutter
Getting Started with Flutter
Getting Started with Flutter
Installation
To get started with Flutter, follow these steps:
Download Flutter SDK: Visit the official Flutter website and download the SDK for your OS.
Set Up Environment: Add Flutter to your PATH and install any required dependencies.
Install Android Studio: Download Android Studio for Android development.
Set Up an Emulator: Create a virtual device for testing your apps.
Hello World App
Let's create a simple "Hello World" app to understand the basics:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Hello World App'),
),
body: Center(
child: Text('Hello, World!'),
),
),
);
}
}This code creates a basic Flutter app with a simple UI displaying "Hello, World!".
Installation
To get started with Flutter, follow these steps:
Download Flutter SDK: Visit the official Flutter website and download the SDK for your OS.
Set Up Environment: Add Flutter to your PATH and install any required dependencies.
Install Android Studio: Download Android Studio for Android development.
Set Up an Emulator: Create a virtual device for testing your apps.
Hello World App
Let's create a simple "Hello World" app to understand the basics:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Hello World App'),
),
body: Center(
child: Text('Hello, World!'),
),
),
);
}
}This code creates a basic Flutter app with a simple UI displaying "Hello, World!".
Installation
To get started with Flutter, follow these steps:
Download Flutter SDK: Visit the official Flutter website and download the SDK for your OS.
Set Up Environment: Add Flutter to your PATH and install any required dependencies.
Install Android Studio: Download Android Studio for Android development.
Set Up an Emulator: Create a virtual device for testing your apps.
Hello World App
Let's create a simple "Hello World" app to understand the basics:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Hello World App'),
),
body: Center(
child: Text('Hello, World!'),
),
),
);
}
}This code creates a basic Flutter app with a simple UI displaying "Hello, World!".
Installation
To get started with Flutter, follow these steps:
Download Flutter SDK: Visit the official Flutter website and download the SDK for your OS.
Set Up Environment: Add Flutter to your PATH and install any required dependencies.
Install Android Studio: Download Android Studio for Android development.
Set Up an Emulator: Create a virtual device for testing your apps.
Hello World App
Let's create a simple "Hello World" app to understand the basics:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Hello World App'),
),
body: Center(
child: Text('Hello, World!'),
),
),
);
}
}This code creates a basic Flutter app with a simple UI displaying "Hello, World!".
Understanding Flutter Basics
Understanding Flutter Basics
Understanding Flutter Basics
Understanding Flutter Basics
Dart Language
Flutter uses Dart, a language optimized for fast apps on any platform. Key features of Dart include:
Optional Typing: Choose between dynamic or static types.
Asynchronous Programming: Built-in support for async/await.
Strong Libraries: Comprehensive core libraries.
Flutter Architecture
Flutter’s architecture is built around the concept of widgets:
Widgets: The building blocks of a Flutter app. They describe what their view should look like.
Composition: Widgets can be composed together to create complex UIs.
Widgets 101
Widgets come in two flavors:
Stateless Widgets: Immutable and cannot change their state once built.
Stateful Widgets: Maintain a state that can change during the app's lifecycle.
Dart Language
Flutter uses Dart, a language optimized for fast apps on any platform. Key features of Dart include:
Optional Typing: Choose between dynamic or static types.
Asynchronous Programming: Built-in support for async/await.
Strong Libraries: Comprehensive core libraries.
Flutter Architecture
Flutter’s architecture is built around the concept of widgets:
Widgets: The building blocks of a Flutter app. They describe what their view should look like.
Composition: Widgets can be composed together to create complex UIs.
Widgets 101
Widgets come in two flavors:
Stateless Widgets: Immutable and cannot change their state once built.
Stateful Widgets: Maintain a state that can change during the app's lifecycle.
Dart Language
Flutter uses Dart, a language optimized for fast apps on any platform. Key features of Dart include:
Optional Typing: Choose between dynamic or static types.
Asynchronous Programming: Built-in support for async/await.
Strong Libraries: Comprehensive core libraries.
Flutter Architecture
Flutter’s architecture is built around the concept of widgets:
Widgets: The building blocks of a Flutter app. They describe what their view should look like.
Composition: Widgets can be composed together to create complex UIs.
Widgets 101
Widgets come in two flavors:
Stateless Widgets: Immutable and cannot change their state once built.
Stateful Widgets: Maintain a state that can change during the app's lifecycle.
Dart Language
Flutter uses Dart, a language optimized for fast apps on any platform. Key features of Dart include:
Optional Typing: Choose between dynamic or static types.
Asynchronous Programming: Built-in support for async/await.
Strong Libraries: Comprehensive core libraries.
Flutter Architecture
Flutter’s architecture is built around the concept of widgets:
Widgets: The building blocks of a Flutter app. They describe what their view should look like.
Composition: Widgets can be composed together to create complex UIs.
Widgets 101
Widgets come in two flavors:
Stateless Widgets: Immutable and cannot change their state once built.
Stateful Widgets: Maintain a state that can change during the app's lifecycle.
Building User Interfaces
Building User Interfaces
Building User Interfaces
Building User Interfaces
Layouts
Flutter offers several layout widgets, including:
Container: A versatile widget for styling and positioning.
Row and Column: Arrange children horizontally or vertically.
Stack: Overlay widgets on top of each other.
Custom Widgets
Creating custom widgets is straightforward:
class CustomButton extends StatelessWidget {
final String label;
CustomButton(this.label);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return RaisedButton(
child: Text(label),
onPressed: () {},
);
}
}Animations and Transitions
Animations enhance user experience. Flutter provides:
Implicit Animations: Simple animations like
AnimatedContainer.Explicit Animations: Detailed animations using
AnimationController.
Layouts
Flutter offers several layout widgets, including:
Container: A versatile widget for styling and positioning.
Row and Column: Arrange children horizontally or vertically.
Stack: Overlay widgets on top of each other.
Custom Widgets
Creating custom widgets is straightforward:
class CustomButton extends StatelessWidget {
final String label;
CustomButton(this.label);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return RaisedButton(
child: Text(label),
onPressed: () {},
);
}
}Animations and Transitions
Animations enhance user experience. Flutter provides:
Implicit Animations: Simple animations like
AnimatedContainer.Explicit Animations: Detailed animations using
AnimationController.
Layouts
Flutter offers several layout widgets, including:
Container: A versatile widget for styling and positioning.
Row and Column: Arrange children horizontally or vertically.
Stack: Overlay widgets on top of each other.
Custom Widgets
Creating custom widgets is straightforward:
class CustomButton extends StatelessWidget {
final String label;
CustomButton(this.label);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return RaisedButton(
child: Text(label),
onPressed: () {},
);
}
}Animations and Transitions
Animations enhance user experience. Flutter provides:
Implicit Animations: Simple animations like
AnimatedContainer.Explicit Animations: Detailed animations using
AnimationController.
Layouts
Flutter offers several layout widgets, including:
Container: A versatile widget for styling and positioning.
Row and Column: Arrange children horizontally or vertically.
Stack: Overlay widgets on top of each other.
Custom Widgets
Creating custom widgets is straightforward:
class CustomButton extends StatelessWidget {
final String label;
CustomButton(this.label);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return RaisedButton(
child: Text(label),
onPressed: () {},
);
}
}Animations and Transitions
Animations enhance user experience. Flutter provides:
Implicit Animations: Simple animations like
AnimatedContainer.Explicit Animations: Detailed animations using
AnimationController.
State Management
State Management
State Management
State Management
Stateful vs Stateless Widgets
Understanding the difference:
Stateless: For static content.
Stateful: For dynamic content that can change.
Managing State
Popular state management solutions include:
Provider: A simple and flexible way to manage state.
Riverpod: An improved version of Provider with better performance.
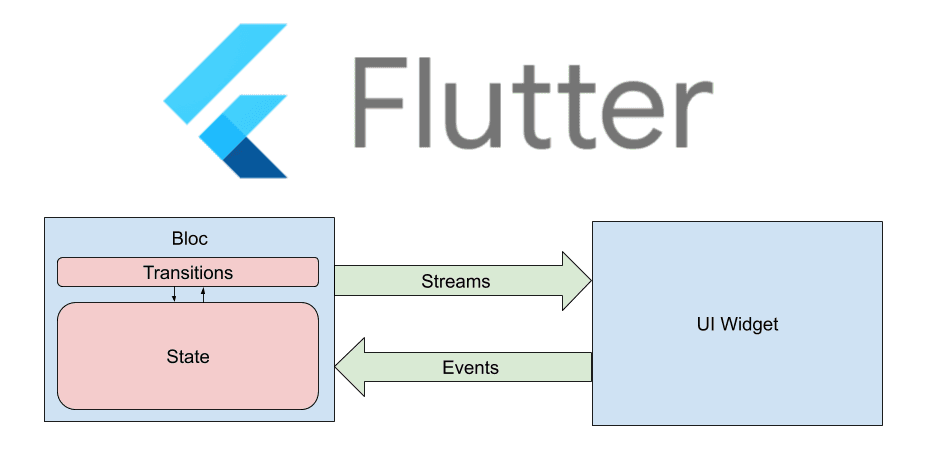
Bloc: Business Logic Component, ideal for large-scale apps.
Stateful vs Stateless Widgets
Understanding the difference:
Stateless: For static content.
Stateful: For dynamic content that can change.
Managing State
Popular state management solutions include:
Provider: A simple and flexible way to manage state.
Riverpod: An improved version of Provider with better performance.
Bloc: Business Logic Component, ideal for large-scale apps.
Stateful vs Stateless Widgets
Understanding the difference:
Stateless: For static content.
Stateful: For dynamic content that can change.
Managing State
Popular state management solutions include:
Provider: A simple and flexible way to manage state.
Riverpod: An improved version of Provider with better performance.
Bloc: Business Logic Component, ideal for large-scale apps.
Stateful vs Stateless Widgets
Understanding the difference:
Stateless: For static content.
Stateful: For dynamic content that can change.
Managing State
Popular state management solutions include:
Provider: A simple and flexible way to manage state.
Riverpod: An improved version of Provider with better performance.
Bloc: Business Logic Component, ideal for large-scale apps.
Handling Navigation and Routing
Handling Navigation and Routing
Handling Navigation and Routing
Handling Navigation and Routing
Navigation Basics
Basic navigation can be implemented using Navigator:
Navigator.push(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) => SecondPage()),
);Advanced Routing
For more complex scenarios:
Named Routes: Define routes in a centralized location.
Deep Linking: Handle URLs to navigate to specific parts of the app.
Navigation Basics
Basic navigation can be implemented using Navigator:
Navigator.push(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) => SecondPage()),
);Advanced Routing
For more complex scenarios:
Named Routes: Define routes in a centralized location.
Deep Linking: Handle URLs to navigate to specific parts of the app.
Navigation Basics
Basic navigation can be implemented using Navigator:
Navigator.push(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) => SecondPage()),
);Advanced Routing
For more complex scenarios:
Named Routes: Define routes in a centralized location.
Deep Linking: Handle URLs to navigate to specific parts of the app.
Navigation Basics
Basic navigation can be implemented using Navigator:
Navigator.push(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) => SecondPage()),
);Advanced Routing
For more complex scenarios:
Named Routes: Define routes in a centralized location.
Deep Linking: Handle URLs to navigate to specific parts of the app.
Networking and Data Handling
Networking and Data Handling
Networking and Data Handling
Networking and Data Handling
HTTP Requests
Use the http package to make network requests:
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
final response = await http.get('https://api.example.com/data');Local Storage
Store data locally using packages like:
SQLite: For complex local storage.
Hive: Lightweight and fast NoSQL database.
SharedPreferences: Key-value storage for simple data.
Real-Time Data
Firebase integration allows real-time updates:
Firestore: Real-time database for synced data.
Firebase Auth: Authentication services.
HTTP Requests
Use the http package to make network requests:
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
final response = await http.get('https://api.example.com/data');Local Storage
Store data locally using packages like:
SQLite: For complex local storage.
Hive: Lightweight and fast NoSQL database.
SharedPreferences: Key-value storage for simple data.
Real-Time Data
Firebase integration allows real-time updates:
Firestore: Real-time database for synced data.
Firebase Auth: Authentication services.
HTTP Requests
Use the http package to make network requests:
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
final response = await http.get('https://api.example.com/data');Local Storage
Store data locally using packages like:
SQLite: For complex local storage.
Hive: Lightweight and fast NoSQL database.
SharedPreferences: Key-value storage for simple data.
Real-Time Data
Firebase integration allows real-time updates:
Firestore: Real-time database for synced data.
Firebase Auth: Authentication services.
HTTP Requests
Use the http package to make network requests:
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
final response = await http.get('https://api.example.com/data');Local Storage
Store data locally using packages like:
SQLite: For complex local storage.
Hive: Lightweight and fast NoSQL database.
SharedPreferences: Key-value storage for simple data.
Real-Time Data
Firebase integration allows real-time updates:
Firestore: Real-time database for synced data.
Firebase Auth: Authentication services.
Testing and Debugging
Testing and Debugging
Testing and Debugging
Testing and Debugging
Unit Testing
Write unit tests to ensure functionality:
void main() {
test('Counter increments smoke test', () {
final counter = Counter();
counter.increment();
expect(counter.value, 1);
});
}Widget Testing
Test the UI components:
testWidgets('Counter increments smoke test', (WidgetTester tester) async {
await tester.pumpWidget(MyApp());
expect(find.text('0'), findsOneWidget);
expect(find.text('1'), findsNothing);
await tester.tap(find.byIcon(Icons.add));
await tester.pump();
expect(find.text('0'), findsNothing);
expect(find.text('1'), findsOneWidget);
});Debugging Tips
Common debugging tools:
Flutter DevTools: Performance and debugging suite.
Dart Observatory: Profiling and debugging tool.
Unit Testing
Write unit tests to ensure functionality:
void main() {
test('Counter increments smoke test', () {
final counter = Counter();
counter.increment();
expect(counter.value, 1);
});
}Widget Testing
Test the UI components:
testWidgets('Counter increments smoke test', (WidgetTester tester) async {
await tester.pumpWidget(MyApp());
expect(find.text('0'), findsOneWidget);
expect(find.text('1'), findsNothing);
await tester.tap(find.byIcon(Icons.add));
await tester.pump();
expect(find.text('0'), findsNothing);
expect(find.text('1'), findsOneWidget);
});Debugging Tips
Common debugging tools:
Flutter DevTools: Performance and debugging suite.
Dart Observatory: Profiling and debugging tool.
Unit Testing
Write unit tests to ensure functionality:
void main() {
test('Counter increments smoke test', () {
final counter = Counter();
counter.increment();
expect(counter.value, 1);
});
}Widget Testing
Test the UI components:
testWidgets('Counter increments smoke test', (WidgetTester tester) async {
await tester.pumpWidget(MyApp());
expect(find.text('0'), findsOneWidget);
expect(find.text('1'), findsNothing);
await tester.tap(find.byIcon(Icons.add));
await tester.pump();
expect(find.text('0'), findsNothing);
expect(find.text('1'), findsOneWidget);
});Debugging Tips
Common debugging tools:
Flutter DevTools: Performance and debugging suite.
Dart Observatory: Profiling and debugging tool.
Unit Testing
Write unit tests to ensure functionality:
void main() {
test('Counter increments smoke test', () {
final counter = Counter();
counter.increment();
expect(counter.value, 1);
});
}Widget Testing
Test the UI components:
testWidgets('Counter increments smoke test', (WidgetTester tester) async {
await tester.pumpWidget(MyApp());
expect(find.text('0'), findsOneWidget);
expect(find.text('1'), findsNothing);
await tester.tap(find.byIcon(Icons.add));
await tester.pump();
expect(find.text('0'), findsNothing);
expect(find.text('1'), findsOneWidget);
});Debugging Tips
Common debugging tools:
Flutter DevTools: Performance and debugging suite.
Dart Observatory: Profiling and debugging tool.
Performance Optimization
Performance Optimization
Performance Optimization
Performance Optimization
Optimizing Performance
Tips for a smoother app:
Avoid Rebuilding Widgets Unnecessarily: Use
constconstructors.Efficient State Management: Use appropriate state management techniques.
Minimize Repaints: Limit the use of
setState.
Best Practices
Code Organization: Follow clean architecture principles.
Consistent Styling: Use themes for a consistent look.
Version Control: Utilize Git for source control.
Deployment
Deploying your app:
Android: Generate a signed APK or App Bundle.
iOS: Create an IPA file and submit to the App Store.
Optimizing Performance
Tips for a smoother app:
Avoid Rebuilding Widgets Unnecessarily: Use
constconstructors.Efficient State Management: Use appropriate state management techniques.
Minimize Repaints: Limit the use of
setState.
Best Practices
Code Organization: Follow clean architecture principles.
Consistent Styling: Use themes for a consistent look.
Version Control: Utilize Git for source control.
Deployment
Deploying your app:
Android: Generate a signed APK or App Bundle.
iOS: Create an IPA file and submit to the App Store.
Optimizing Performance
Tips for a smoother app:
Avoid Rebuilding Widgets Unnecessarily: Use
constconstructors.Efficient State Management: Use appropriate state management techniques.
Minimize Repaints: Limit the use of
setState.
Best Practices
Code Organization: Follow clean architecture principles.
Consistent Styling: Use themes for a consistent look.
Version Control: Utilize Git for source control.
Deployment
Deploying your app:
Android: Generate a signed APK or App Bundle.
iOS: Create an IPA file and submit to the App Store.
Optimizing Performance
Tips for a smoother app:
Avoid Rebuilding Widgets Unnecessarily: Use
constconstructors.Efficient State Management: Use appropriate state management techniques.
Minimize Repaints: Limit the use of
setState.
Best Practices
Code Organization: Follow clean architecture principles.
Consistent Styling: Use themes for a consistent look.
Version Control: Utilize Git for source control.
Deployment
Deploying your app:
Android: Generate a signed APK or App Bundle.
iOS: Create an IPA file and submit to the App Store.
Conclusion
Conclusion
Conclusion
Conclusion
Recap
We've covered the essentials of Flutter app development, from setup to deployment, ensuring you have the knowledge to build robust and performant apps.
Resources
Recap
We've covered the essentials of Flutter app development, from setup to deployment, ensuring you have the knowledge to build robust and performant apps.
Resources
Recap
We've covered the essentials of Flutter app development, from setup to deployment, ensuring you have the knowledge to build robust and performant apps.
Resources
Recap
We've covered the essentials of Flutter app development, from setup to deployment, ensuring you have the knowledge to build robust and performant apps.
Resources
Table of content
© 2021-25 Blupx Private Limited.
All rights reserved.
© 2021-25 Blupx Private Limited.
All rights reserved.
© 2021-25 Blupx Private Limited.
All rights reserved.